CBD in Canada has become a pretty common household name over the past couple of years. If you’re looking for the benefits or CBD, CBG, and CBN in Canada, explore them with us in detail. The potential benefits from CBD, CBG, CBN have garnered a lot of media attention and for a good reason. But what are cannabinoids? Many people still aren’t quite sure of what CBD is exactly. or how different cannabinoids work in the body.
CBD comes from cannabis, and most commonly, the hemp plant. While hemp and marijuana are both classified as cannabis, though there is a crucial difference between the two; hemp is low in THC, the compound that gets you stoned, and high in CBD. Marijuana, on the other hand, is the exact opposite.
In this article, we’ll explain and go over:
- What cannabinoids are and how they work in the body
- The many different cannabinoids that are in hemp
- What these cannabinoids are used for
- What synthetic cannabinoids are
Learning and understanding what these cannabinoids can do and how they may benefit you is an important part of taking CBD.
What are cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are compounds that are found within the hemp plant; to date there are over 100 that have been identified. At the same time, research on some of them like CBD and THC, is vast; others such as CBG and CBN are just starting to be fully explored.
Phytocannabinoids (plant cannabinoids) work by mimicking the cannabinoids that our bodies produce, called endocannabinoids. Our bodies naturally produce two different endocannabinoids:
- Anandamide
- 2-arachidonoylglyerol
Phytocannabinoids are very similar in chemical makeup to these naturally occurring endocannabinoids and impact our system in much the same way.
Research shows that cannabinoids have the potential to help many ailments in the human body, such as anxiety, pain, inflammation, and may even help fight cancer. These cannabinoids help keep everything in balance by way of the Endocannabinoid System
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The Endocannabinoid System is a vast network that runs throughout our bodies and brains. One of its jobs, and arguably the main one, is to keep everything running smoothly, called homeostasis.
When ingested, cannabinoids travel along the Endocannabinoid System and attach to receptors that are found there, called CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors live mainly within the brain and the body’s central nervous system; CB2 receptors are located mainly throughout the immune and digestion systems.
Different cannabinoids will produce different responses, depending on what they are and which receptor they bind to. In particular, these receptors are responsible for telling the cell that it is attached to how to function or make changes.
The Endocannabinoid is thought to impact many other important systems in our bodies. Because of this, the discovery of cannabinoids and how they function is very important. Some of the things that it affects are:
- Mood
- Memory
- Reproduction
- Body temperature
- Immune function
- Appetite and digestion
- Sleep
- Motor control
- Liver function
- Stress
- Skin
As you can see, the Endocannabinoid System is pretty crucial to how our bodies function as a whole. In general, by supplementing with cannabinoids like CBD, you can positively impact these functions.
What cannabinoids are in hemp?
Throughout the decades, the most popular (and controversial) cannabinoid that has garnered most of the attention is THC. It was only more recently, in the ’90s, that scientists discovered the Endocannabinoid System, and the attention began to shift to other cannabinoids.
While there have been 113 different cannabinoids identified in cannabis, not all are found in high quantities. Because of this, scientists are focusing on just a few, many of which show promise in treating many medical conditions.
CBD (cannabidiol)
CBD is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in great quantities in the hemp plant and has vast medical implications. It has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antioxidant properties. Moreover, it may help relieve anxiety, fight pain, reduce inflammation, and has neuroprotective properties that show its effectiveness at treating debilitating diseases such as Alzheimer’s. CBD binds more to CB2 receptors, though recent research shows that it binds poorly; more study in the field is necessary to unlock its full potential.
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)
THC is most commonly known for its ability to produce mind-altering effects when you ingest it. It acts primarily on CB1 receptors in the brain and may reduce pain, nausea and help fight cancer cells. THC is found in meager quantities in hemp and is more prominent in marijuana.
THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin)
Similar to THC, THCV is a psychoactive cannabinoid, but one that differs slightly in the effects that it produces. It has a higher boiling point to it than THC (220 °C), and is found in lesser quantities. Emerging research shows that it may reduce appetite, stimulate bone growth, and could potentially help fight Alzheimer’s.
CBG (cannabigerol)
Known as the mother of all cannabinoids, CBG is the precursor to all cannabinoids. CBGA, the acidic form of CBG, breaks down into 3 main cannabinoids as it ages, CBD, THC, and CBC. CBG is thought to provide relief from inflammation, may help glaucoma, and has been shown through studies to have an anti-tumor effect.
CBN (cannabinol)
This cannabinoid has gained a reputation as the “sleepy cannabinoid” and is commonly found in CBD oil sleep formulas. CBN is thought to have more sedating effects; this cannabinoid is very mildly psychoactive and results from the degradation of THC. CBN isn’t abundant in hemp; thus, it makes it a more expensive cannabinoid to extract. While CBN is rumored to have more sedating effects, the research on this isn’t conclusive.
CBC (cannabichromene)
Research shows that CBC may help promote bone growth, reduce pain and inflammation, and fight cancer cells. It is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that doesn’t directly interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors. Instead, CBC binds with the vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) and the transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1). Both of these receptors are associated with pain and the perception of pain.
Acidic vs Active Cannabinoids
All cannabinoids start in their acidic forms. It is only through a process called decarboxylation, or heating, that cannabinoids transform into their active forms.
- THCA > THC
- CBDA > CBD
- CBCA > CBC
- CBGA > CBG
Decarboxylation is essentially the heating of the material. Take THC, for example. In its acid state, THCA is non-psychoactive; when you heat it by smoking or vaping, it then becomes a psychoactive compound.
CBGA is unique in the fact that it both breaks down into other cannabinoids (THCA, CBDA, CBCA) through aging and certain enzymes in cannabis but also decarbs into CBG. THC is also unique in that as it ages, it can turn into CBN. There is research that shows CBN to have slight psychoactive properties, though they are very minimal.
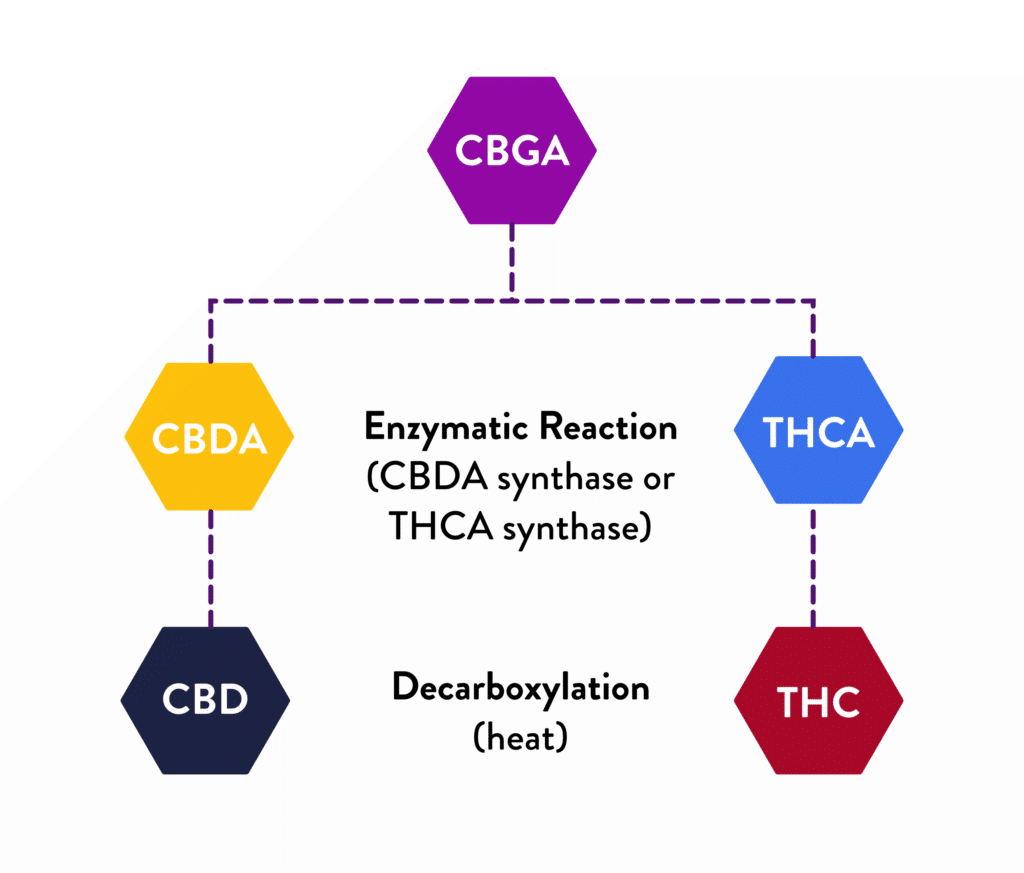
Depending on how these cannabinoids are used, be it their acidic forms or active, they may affect the body differently. CBDA, for example, shows to be much more effective at reducing nausea than CBD. Those looking for the benefits of THC, and not the high, may find THCA to be the better option for them.
What are cannabinoids used for?
CBD may seem like it has the most potential benefits to offer, but it isn’t responsible for these all by itself. Science says that when used together, cannabinoids offer greater benefits than any one of the cannabinoids on its own due to the Entourage Effect.
Considered to be one of the biggest breakthroughs in recent medical history, the discovery of the Endocannabinoid System and its potential to treat all sorts of ailments has hit the world in full force.
Some of the disorders, diseases, and ailments that cannabinoids may be able to treat are:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- PTSD
- IBS/IBD
- Migraines
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- MS
- Cancer
- Inflammation
- Insomnia
- Chemotherapy side effects
- Nerve pain
- Muscle recovery
- Joint pain
- Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Alzheimer’s
- Dementia
- Weight loss
- Acne
- Epilepsy
- Fatigue
- Chronic pain
- Arthritis
- Stress
- Fibromyalgia
- Nausea
- Addiction
- Diabetes
What are synthetic cannabinoids?
Synthetic cannabinoids bind to the same THC, and CBD receptors do, but they do not come from plants. Instead, they are human-made chemicals that may lead to serious adverse effects if used in the wrong way.
While scientists are exploring how synthetic CBD may be used, many are skeptical, however; this is largely due to the vape cart scare in 2019. This resulted in numerous people falling ill and 19 people dying from lung issues related to vaping black market THC products.
While we may in the future be able to recreate these compounds to be just as good, higher levels of bromide and fluoride are a big cause for concern right now.
Generally speaking, sourcing and using the natural compounds from the plant, and not from something synthesized in a lab, is the only way to go.
While many claim to get great benefits from CBD oil alone, other cannabinoids like CBG and CBN may be an addition that could help boost the effects of your oil.
We’ve learned that the Entourage Effect plays a big part in how effective cannabinoids can be when used together; it only makes sense to incorporate them into our daily routines.
Ready to start exploring other cannabinoids beside CBD? Check out these popular oil blends available on site now:



Comments are closed.